Covid impact: Jobless rate to hit 8.5% if stimulus not widened, says Pronab Sen
While unemployment is essentially in the urban areas, it is difficult to estimate due to reverse migration, Sen said.
The national employment-unemployment survey report released on Thursday showed India’s unemployment rate fell to 5.8% between July 2018 and June 2019 from a more than four-decade high of 6.1% in the same period in 2017-18.
“The estimate for this year depends on what the government does. If this is the only stimulus, then the overall unemployment could be 8-8.5%,” he said.
Independent think tank Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy said earlier that the unemployment rate shot up to 23.48% in May this year from 7.87% in June 2019.
Sen heads the government’s one-man standing committee on economic statistics (SCES) set up to deliberate and develop methodologies for surveys on industry, services and employment in place of multiple panels on these issues.
The government has unveiled a ₹20-lakh crore relief package, including liquidity measures by the Reserve Bank of India to counter the impact of the nationwide lockdown. The RBI has cut rates twice to record lows besides providing liquidity support and regulatory relief.
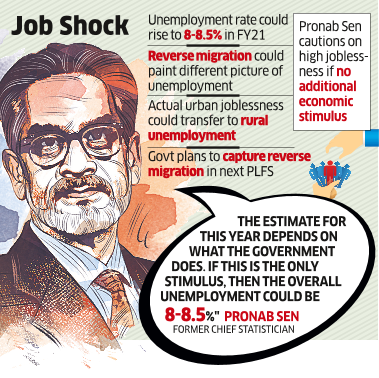
While rural unemployment may not actually be as bad as urban because agriculture is doing well, Sen said migration to rural areas may push it up.
“If people move back to rural areas during the survey time then rural unemployment will increase and urban employment would seem to be lower,” Sen said, explaining that rural unemployment is usually around 2.2-2.3% while urban unemployment is in the 8-9% range.
There has been a largescale reverse migration from cities over the last two months.
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) is examining changes that may need to be carried out to assess the extent of unemployment following the reverse-migration in the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), to get a better sense of employment given the large migration.





